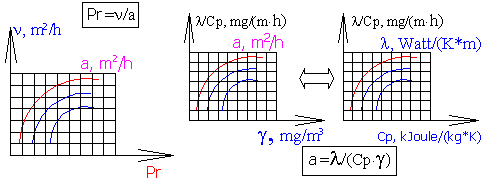Graphic-analytical calculation of criterion Pr
graphoanalytical calculation of the Prandtl number
The Prandtl number characterizes the influence of the physical properties of the medium on the heat transfer process and is determined by its thermodynamic state.
Criterion Pr - thermalphysic constant of substance. Formula for calculating the Prandtl number
Pr = υ / a
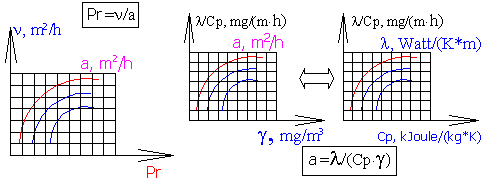
Scheme of the system of nomograms for the graphic-analytical calculation of the Prandtl number
|
Designations in the Pr calculation formula and on nomograms:
a
- coefficient of temperature conductivity, m2/h,
n
- coefficient of kinematic viscosity,
m2/h,
g
- specific gravity, mg/m3,
Ñð
- thermal (heat) capacity
at constant pressure, kJoule/(kg*Ê) [kkal/(g*grad)],
l
- coefficient of thermal conductivity,
Watt/(m*Ê) [kal/(m*h*grad)],.
|
The Prandtl number Pr consists of quantities characterizing the thermophysical properties of a substance (medium) and, in essence, is itself a thermophysical constant of a substance.
Thermal diffusivity a characterizes the rate of temperature equalization in nonequilibrium processes.
Thermal conductivity coefficient l characterizes the ability of a substance to conduct heat.
Specific heat capacity Cp characterizes the ability of a substance to absorb ("absorb") heat when the temperature rises, which can be roughly compared with the ability of an electric capacitor to store energy.
The coefficient of kinematic viscosity υ characterizes the viscous state of a substance, taking into account the influence of gravity.
Viscosity is the state of "internal friction" of a substance (friction between layers of liquid or gas), which is expressed in the "internal resistance" of the liquid to the process of its movement, more precisely, the resistance to the movement of some layers of the liquid relative to others.
Systems of nomograms for graphic-analytical calculation of the Prandtl number
|
nomogram systems for calculating the number Pr contain the following ranges of parameter values:
l - (0.01 ... 0.85) Watt/(m*Ê)
Ñð - (0.02 ... 20) kJoule/(kg*Ê)
g - (0.001
... 40) mg/cm3
n - (0.001 ... 5) m2/h a
- (0.005 ... 0.8) m2/h Pr - 0.2 ... 220 |
To convert between systems of units, we use the following relations
1 kal = 4.1868
Joule;
1
Watt/(m*Ê) = 860 [kal/(m*h*grad)]
1 Watt
· h = 3600 Joule
Thermal (heat) capacity (Ñð) of hydrogen at temperature 300 Ê and pressure
1 kgf/cm2 - Ñð=3.42 kal/(g*grad).
Translation - Ñð=3.42*4.1868 = 14.319 kJoule/(kg*Ê).
Thermal (heat) conductivity (l) of hydrogen under the same conditions
l = 158 kal/(m*h*grad), that corresponds
l = 158/860=0.184 Watt/(m*Ê).
Dynamic viscosity
(n) for
xenon under normal conditions - n=2*10-4 m2/s. Transformation: n=2*10-4
*3600=0.72 [m2/h] |
graphic-analytical systems
The contact information: nomogramka@gmail.com
Copyright © 2005-2022 All rights reserved