Calculation of the characteristics of the throttling channel made in the form of a coil (laminar flow regime)
Graph-analytical calculation of a laminar choke-coil
Laminar flow is the movement of a viscous liquid or gas, in which the individual layers of the current substance slide relative to each other without mixing.
 |
G
= 200 ... 1500 mg/s
P02
- P12 = 0 ... 4000 kgf2/cm4
d
= 0.2 ... 2.0 mm
Re
= 150 ... 450 |
|
G
= 200 ... 1500 mg/s
P02
- P12 = 0 ... 3500 kgf2/cm4
d
= 0.5 ... 2.3 mm
Re
= 700 ... 1950 |
|
G
= 300 ... 1500 mg/s
P02
- P12 = 300 ... 4500 kgf2/cm4
d
= 0.3 ... 1.2 mm
Re
= 1900 ... 2800 |
|
G
= 2 ... 100 mg/s
P02
- P12 = 1 ... 100 kgf2/cm4
d
= 0.3 ... 0.9 mm
Re
= 250 ... 1000 |
|
G
= 20 ... 100 mg/s
P02
- P12 = 10 ... 210 kgf2/cm4
d
= 0.3 ... 1.0 mm
Re
= 1000 ... 2300 |
|
G
= 20 ... 100 mg/s
P02
- P12 = 10 ... 220 kgf2/cm4
d
= 0.4 ... 0.7 mm
Re
= 1300 ... 2200 |
The calculation of the hydraulic characteristics of the throttling channel (a choke tube bent in the form of a coil) is performed without taking into account heat exchange with the environment.
To calculate the heat transfer processes of a serpentine laminar throttle (taking into account the diameter of the throttling channel and the temperature of the working fluid obtained (or accepted)
during this graphic-analytical calculation), it is necessary to use the appropriate systems of nomograms in the "Heat engineering calculations" section.
A laminar throttle is a throttling channel (pipeline, capillary), in which the length significantly exceeds the transverse dimension (the diameter of the cylindrical channel).
Parameters of graphoanalytical calculation of spiral laminar choke (serpentine type)
The presented system of nomograms allows you to select or calculate the following characteristics of a pipeline (or capillary) bent in the form of a coil:
- d, mm
- internal diameter of the laminar channel;
- L, cm
- length of the laminar channel;
- R, mm
- radius of a coil;
- Re
- number Re;
- lambda
- factor of hydraulic losses;
- T, K
- temperature of gas;
- R, kg·m/kg·K
- gas constant;
- G, mg/c
- the charge of gas;
- P0, kgs/cm2
- pressure upon an input in the laminar channel-coil;
- P1, kgs/cm2
- pressure upon an output from the laminar channel-coil.
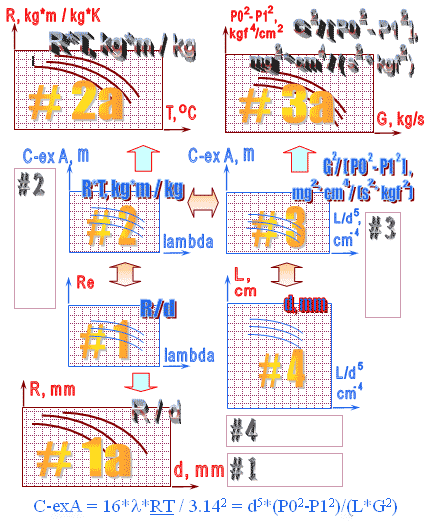
Description of work with the system of nomograms when carrying out graphic-analytical calculation of an extended throttling channel of a spiral shape (coil)
When calculating, it is necessary to form a system of nomograms, the layout of which is shown in the figure, from two halves - left and right.
Each of the six options above has several left and several right parts that differ in parameter ranges.
When you call up variants of these parts, they remain on the screen.
They can be hidden by moving the border of the window in which this part is located. In some parts there are no auxiliary charts (additional nom.).
This means that they repeat the auxiliary charts present in the previous version.
They can be viewed by opening this option (by moving the window border to view).
On the main and auxiliary nomograms, graphs of the same color have the same parameter values.
Graphs on nomogram #1 have a section close to horizontal ("step") - these sections are clearly visible when opening the system of nomograms #1.
At this point, the formula for calculating the hydraulic resistance changes when certain conditions are reached.
With an increase in the value of hydraulic resistance and a decrease in the Reynolds number, each graph ends with a rather long "shelf", the shape of which is close to horizontal.
Left point "shelves" of all graphs is on a common graph expressing the graphic dependence for the straight channel (lambda = 64/Re) - straight throttle tube,
i.e. the case of degeneration of the coil into a "linear pipeline".
The procedure for calculating a curved extended pipeline with a laminar flow regime
1. As a first approximation, we set any of the listed parameters.
2. Using a system of nomograms with a suitable range of parameters, we find the values of the missing characteristics.
3. We correct the given (or accepted in the first approximation) parameters and find the remaining characteristics in the next approximation.
An example of hydraulic calculation of the parameters of a capillary coil with a laminar flow of a gaseous working fluid
Condition 1.
The gas mixture flow rate is 500 mg/s. The pressure in the cylinder (at the coil inlet) is 30 kgf/cm2.
The pressure at the outlet of the coil is 1 kgf/cm2.
The average temperature of the gas mixture in the coil channel is 310 K.
For design reasons, the radius of the coil should be 12.5 mm.
The gas constant of a mixture of gases is R=910 kg·m/kg·K.
Determine the design characteristics of a curved capillary pipeline.
Calculation.
We choose the inner diameter of the throttling channel in the first approximation - d = 2 mm.
We calculate the ratio R/d = 4. Determine the value P02 - P12 = 899 kgf2/cm4.
We select the system of nomograms #1 for calculation. We select the right part #3.
On the auxiliary nomogram #3a, we find a graph for the ratio of the flow rate and the difference in the square of pressures.
The value is between the graphs with the values ??of 250 and 350 mg2 cm4/[s2 kgf2] and is approximately equal to 280 mg2 cm4/[s2 kgf2].
As a first approximation, we take the length of the capillary channel L = 50 cm.
We find the intermediate value L/d4 = 1.5 105 cm-4 (X axis) on nomogram #4 for the selected values ??of the length of the throttling channel (50 cm) and diameter (2 mm).
On nomogram #3 we find the approximate value of the expression C-ex A = 2.35 105 m.
Select the left side #1. On the auxiliary nomogram #2a we find a graph that satisfies the given values ??of temperature (310 K) and gas constant (910 kg m/kg K).
This is a graph with an RT value of 37 kg m/kg.
On the nomogram #2 for this graph and the value of C-ex A = 280 mg2 cm4/[s2 kgf 2] (Y axis), we find the approximate value of the coefficient of hydraulic resistance lambda = 0.387.
On the auxiliary nomogram #1a, we find a graph that satisfies the selected value of the inner diameter and the given value of the coil radius.
We will get a graph with the value R/d = 6. On the nomogram #1, we determine the Re value (Y axis) for the R/d = 6 graph with a value of lambda = 0.387 (X axis).
Approximate value of Re = 223.
So, as a result of a graphical-analytical calculation using a system of nomograms, the following values of the parameters of a laminar coil type choke were obtained:
d = 2 ìì, L = 50 ñì, Re = 223.
Section topic: calculation of a curved extended pipeline - a laminar choke type coil.
Section nomogram systems can be used in combination with nomogram systems of the section "Thermal calculations" to calculate the heat losses of the coil.
Throttle puck calculation (gas flow) is given on the page "Throttle calculation".
The calculation of the jet (fluid flow) is given on the page "Jet calculation".
graphic-analytical systems
The contact information. E-mail: nomogramka@gmail.com
Copyright © 2005-2022 All rights reserved
