Graph-analytical calculation of the Reynolds number Re (using nomogram systems No. 1)
The Reynolds number characterizes the ratio of inertial forces to viscous friction forces, which can be represented as the ratio of the kinetic energy of the flow to the energy losses in a certain area.
The critical Reynolds number (for smooth straight pipes is approximately 2300) separates the flow of matter into laminar and turbulent.
Less than the critical number - laminar, more - turbulent.
The Reynolds criterion is named after the eminent physicist Osborne Reynolds (1842 - 1912) for his work in fluid dynamics related to this criterion.
The concept of criterion was defined by George Stokes in 1851. Named "Reynolds' criterion" by Arnold Sommerfeld in 1908.
Notation used in calculating the Reynolds criterion
m -
dynamic viscosity coefficient:
- in engineering units - x106, kg·s/m2 - e.g. for air m = 1,81·10-6 kg·s/m2,
- in SI units
- x105, Pa·s [kg/(s·m)] - e.g. for air m = 1,81·10-5 Pa·s;
d - channel diameter (hydraulic diameter), mm;
G - mass flow rate of the working substance, g/s.
Reynolds number (Re) formula
- for m in technical units - Re = 4·G/[3,14·d·m·g],
- for m in SI
- Re = 4·G/[3,14·d·m],
where g - free fall acceleration, m/s2.
When you select m (on the upper nomogram) we are looking for the numerical part of the dynamic viscosity coefficient, regardless of the system of units (technical or SI) - nothing needs to be recalculated. For air it is 1.8.
|
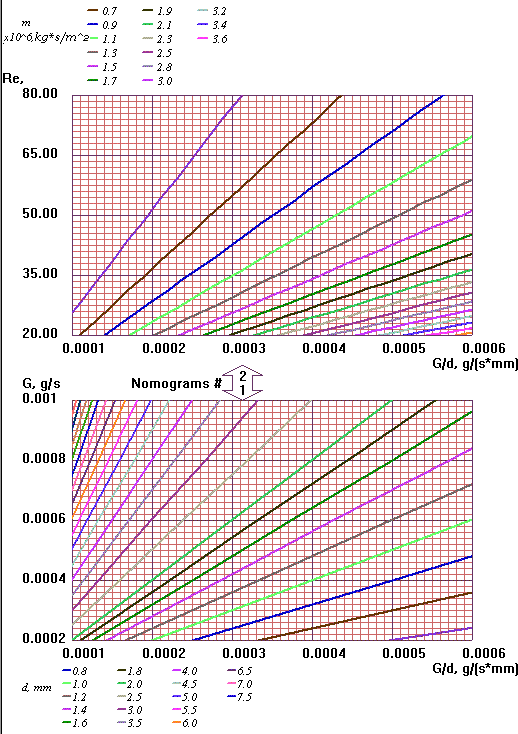
 Nomogram #1
Nomogram #1
d = 0,4 ... 7,5 mm
G = 0,2 ... 1 mg/s
Re= 20 ... 80 |
|
 Nomogram #2
Nomogram #2
d = 1,8 ... 12,5 mm
G = 40 ... 200 mg/s
Re= 600 ... 3000 |
|
 Nomogram #3
Nomogram #3
d = 0,4 ... 9,5 mm
G = 0 ... 200 mg/s
Re= 1000 ... 3000 |
|
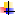 Nomogram #4
Nomogram #4
d = 1,8 ... 12,5 mm
G = 40 ... 200 mg/s
Re= 1000 ... 3000 |
|
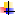 Nomogram #5
Nomogram #5
d = 0,6 ... 12,5 mm
G = 10 ... 90 mg/s
Re= 200 ... 800 |
|
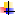 Nomogram #6
Nomogram #6
d = 2,5 ... 12,5 mm
G = 200 ... 1000 mg/s
Re= 800 ... 2400 |
|
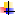 Nomogram #7
Nomogram #7
d = 2,5 ... 12,5 mm
G = 200 ... 1000 mg/s
Re= 2500 ... 8500 |
Dynamic viscosity (dynamic viscosity coefficient) determines the level of viscosity of the substance, i.e. the state of "internal friction" of a certain substance (is a property ("nature")
of this particular substance)
The dynamic viscosity factor is the proportionality factor in Newton's law of viscosity (1867)
graphic-analytical systems
The contact information. E-mail: nomogramka@gmail.com
Copyright © 2005-2022 All rights reserved

![]() Nomogram #1
Nomogram #1